Ch13-26~27. suspend()...
0. 목차
Chapter13. 쓰레드
Ch13 - 26. suspend(), resume(), stop()
Ch13 - 27. suspend(), resume(), stop() 예제
Ch13 - 26. suspend(), resume(), stop()
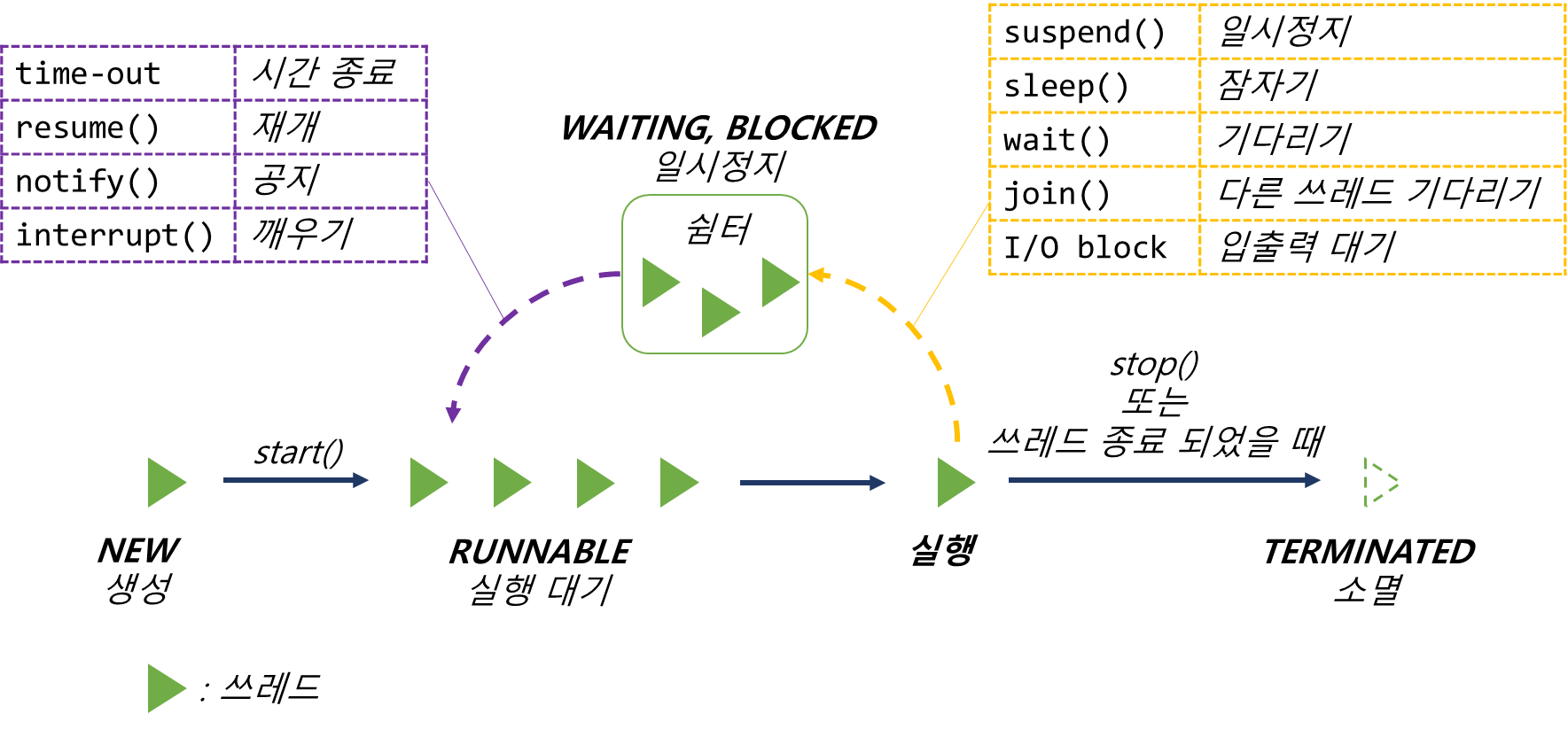
▶ void suspend()
▷ 쓰레드의 실행을 일시정지
▶ void resume()
▷ 쓰레드의 실행을 재개
▶ void stop()
▷ 쓰레드의 실행을 완전정지
▶ suspend(), resume(), stop() = deprecated
▷ dead-lock 교착 상태에 빠질 가능성이 높기 때문
class ThreadEx17 implements Runnable {
boolean suspended = false;
boolean stopped = false;
public void run() {
while(!stopped) { // stop()이 수행X false -!false→ true
if(!suspended) { // suspend()이 수행X false -!false→ true
// 쓰레드가 수행 할 코드 작성
}
}
}
public void suspend() { suspended = true; }
public void resume() { suspended = false; }
public void stop() { suspended = true; }
}
Ch13 - 27. suspend(), resume(), stop() 예제
▶ th1, th2, th3 반복하다 일시정지, 재개, 완전 종료
▷ suspend(), resume(), stop()
class Ex13_10 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
RunImplEx10 r = new RunImplEx10();
Thread th1 = new Thread(r, "th1");
Thread th2 = new Thread(r, "th2");
Thread th3 = new Thread(r, "th3");
th1.start();
th2.start();
th3.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
th1.suspend(); // th1 일시정지
Thread.sleep(2000);
th2.suspend(); // th2 일시정지
Thread.sleep(3000);
th1.resume(); // th1 재개
Thread.sleep(3000);
th1.stop(); // th1 완전 종료
th2.stop(); // th2 완전 종료
Thread.sleep(2000);
th3.stop(); // th3 완전 종료
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
} // main
}
class RunImplEx10 implements Runnable {
public void run() {
while(true) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
}
}
}
// console
// suspend(), resume(), stop() 반복적으로 발생
th2
th1
th3
th1
th2
th3
th2
th3
th1
th3
th2
th3
th2
th3
th3
th3
th1
th1
th3
th1
th3
th2
th3
th3
▷ suspend(), resume(), stop() = deprecated
▷ 그래서 run에서 오버라이딩 해 주기
class Ex13_10 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
MyThread th1 = new MyThread("th1");
MyThread th2 = new MyThread("th2");
MyThread th3 = new MyThread("th3");
th1.start();
th2.start();
th3.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
th1.suspend(); // 쓰레드 th1을 잠시 중단시킨다.
Thread.sleep(2000);
th2.suspend();
Thread.sleep(3000);
th1.resume(); // 쓰레드 th1이 다시 동작하도록 한다.
Thread.sleep(3000);
th1.stop(); // 쓰레드 th1을 강제종료시킨다.
th2.stop();
Thread.sleep(2000);
th3.stop();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
} // main
}
class MyThread implements Runnable {
volatile boolean suspended = false;
volatile boolean stopped = false;
Thread th;
MyThread(String name) {
th = new Thread(this, name); // Thread(Runnable r, String name)
}
void start() {
th.start();
}
void stop() {
stopped = true;
}
void suspend() {
suspended = true;
}
void resume() {
suspended = false;
}
public void run() {
while (!stopped) {
if (!suspended) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
} // run()
}
// console
th1
th3
th2
th1
th3
th2
th3
th1
th2
th3
th2
th3
th3
th3
th1
th3
th1
th3
th1
th3
th3
th3
- volatile
- 자주 변경되는 변수 앞에 붙임
- RAM의 메모리를 CPU Core에 있는 Chache가 복사해서 사용
- 근데 복사가 하다가 true로 변경되었는데 false 되어있고 이런 실수 발생
- 변경이 많으면 실수 발생 가능성↑
- 그래서 변경많은 변수니까 원본으로 바로 쓰겠다고 해 주는 수식어
- 자주 변경되는 변수 앞에 붙임